Lorazepam, haloperidol considerably cut back end-of-life delirium
August 26, 2025
4 min learn
Key takeaways:
- Lorazepam and haloperidol can considerably lower agitation associated to end-of-life delirium for sufferers with most cancers.
- Lorazepam diminished agitation probably the most, and haloperidol had a decrease impact.
Each lorazepam and haloperidol can be utilized to considerably cut back agitation associated to end-of-life delirium for sufferers with most cancers, however the magnitude of their impression differed considerably.
Outcomes of a randomized medical trial confirmed scheduled lorazepam diminished agitation probably the most, however haloperidol might be an choice for households preferring a milder impact.

Information have been derived from Hui D, et al. JAMA Oncol. 2025;doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2025.2212.

David Hui
“Completely different medicines have totally different ranges of sedation,” David Hui, MD, MSc, FAAHPM, director of supportive and palliative care analysis at The College of Texas MD Anderson Most cancers Middle, advised Healio. “We will use this information to personalize the look after our sufferers experiencing this very troublesome syndrome.”
Distressing for all
Greater than 90% of sufferers with most cancers expertise delirium within the remaining weeks of their life, and between 50% to 70% of them additionally develop restlessness and/or agitation, in keeping with research background.
“When sufferers are getting weaker and weaker within the hospital, they typically develop confusion or delirium” Hui stated. “They’re typically not in a position to management their behaviors or how they work together with others and that may trigger a number of misery, not solely within the sufferers themselves, who could also be semi-aware, but additionally within the caregivers and, to a sure extent, the well being care professionals.”
Most people with end-of-life delirium expertise it till demise. Non-pharmacological interventions corresponding to correct hydration; minimizing stimulation at night time to advertise higher sleep; orientation cues corresponding to open home windows in the course of the day, seen dates, occasions and household photos; and availability of listening to and visible aids typically have restricted impact.
“Whereas there’s good proof to help that these measures might forestall the event of delirium at earlier levels of sickness, the state of affairs may be very totally different for end-of-life delirium when the mind is failing as demise approaches,” Hui stated.
People who’re already experiencing end-of-life delirium typically want extra help. Neuroleptics and benzodiazepines may be efficient, however questions persist concerning the dangers and advantages.
“Due to that, we determined to do that research to match 4 alternative ways of managing this agitated delirium within the palliative care setting to see how we may help sufferers higher,” Hui stated.
Hui and colleagues randomly assigned 72 sufferers (imply age, 64 years; normal deviation, 12; 58% males; 59.7% white) 1:1:1:1 to obtain scheduled haloperidol (n = 16), lorazepam (n = 19), haloperidol and lorazepam (n = 18), or placebo (n = 18) to research.
Members obtained scheduled IV doses each 4 hours and rescue treatment each hour, if mandatory.
These within the placebo arm additionally obtained lorazepam firstly of the blinded section and as a rescue treatment for moral causes.
Change in Richman Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS) rating over the primary 24 hours of therapy served as the first endpoint. Use of rescue medicines served as the important thing secondary endpoint.
‘Customized sedation objectives’
All sufferers had important decreases in RASS rating in the course of the first hour of therapy, and so they stayed considerably decrease all through the primary 24 hours.
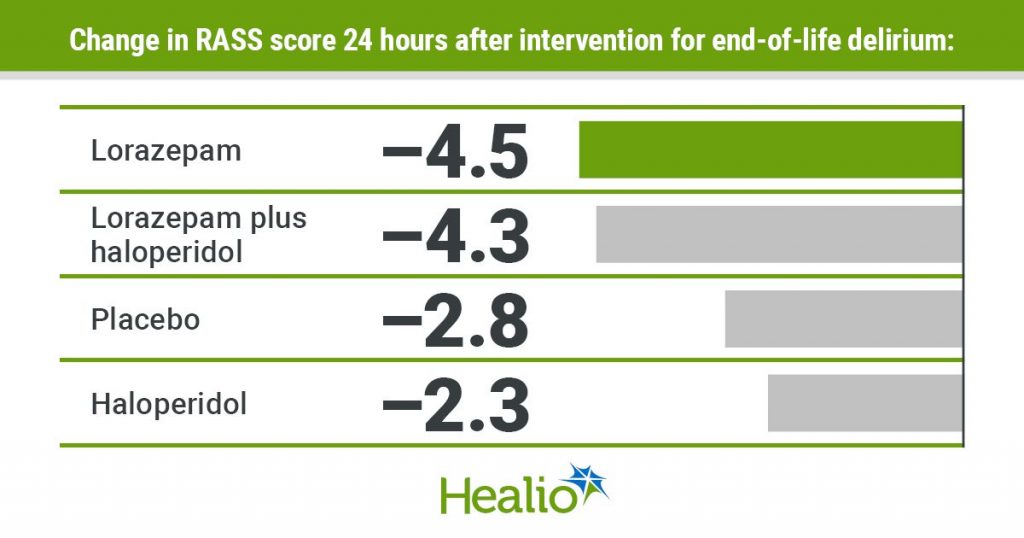
At 24 hours, sufferers who obtained lorazepam had the best discount in RASS rating (change = –4.5; 95% CI, –5.3 to –3.6), adopted by the mixture arm (change = –4.3; 95% CI, –5.2 to –3.4), placebo (change = –2.8; 95% CI, –3.7 to –1.9) and haloperidol (change = –2.3; 95% CI, –3.2 to –1.5).
Researchers discovered people who obtained lorazepam had a considerably better discount in RASS rating than those that acquired haloperidol (imply distinction = –2.1; 95% CI, –3.4 to –0.9), as did those that acquired the mixture therapy (imply distinction = –2; 95% CI, –3.2 to –0.8).
They didn’t discover a important distinction between lorazepam and the mixture, nor haloperidol and placebo.
Considerably fewer contributors who obtained the mixture remedy (32%) or lorazepam alone (37%) wanted rescue doses in contrast with those that acquired haloperidol (56%) or placebo (83%; P = .006).
Nurses seen people who obtained mixture remedy (60%) or lorazepam (68%) to be considerably extra comfy than those that obtained haloperidol (92%) or placebo (100%; P = .009).
Nurses additionally felt those that acquired the mixture (67%) or lorazepam (68%) to be considerably much less agitated in contrast with those that acquired haloperidol (92%) or placebo (100%; P = .02).
Hui famous the general numbers confirmed related outcomes for haloperidol and placebo, however the preliminary dose of lorazepam for sufferers within the placebo arm must be thought-about.
“In the event you take a look at the curve all through the primary 24 hours, you see the placebo group dipped when it comes to their agitation, and that is smart — we imagine it’s the lorazepam impact,” he stated. “Then the extent of agitation begin to climb up over time, suggesting the lorazepam impact is weaning off. That’s when sufferers require extra breakthrough restlessness. With out the rescue medicines, we imagine the placebo group will clearly be quite a bit worse. If I have been treating a affected person with persistent agitated delirium, I’d not prescribe solely as wanted treatment with out something scheduled.”
The commonest extreme opposed occasions included hypotension (26%) and hypoxia (26%), however researchers didn’t observe a big distinction between arms.
“That is reassuring,” Hui stated. “Medicines may be given even to this very sick inhabitants.”
Researchers acknowledged research limitations, together with give attention to the end-of-life setting.
“If we give these medicines within the for much longer time period, we would begin to see extra negative effects,” Hui stated.
Hui and colleagues are persevering with their analysis with an investigation of “personalised sedation objectives.”
“We ask the caregivers, ‘What stage of RASS rating do you assume can be most applicable for your loved ones who’s going by means of this?’” Hui stated. “Then, they weigh the dangers and advantages and inform us which RASS stage they like. The secret is then to see, can we match their objective with proper therapy to supply objective concordant care?”
The search can also be on for newer or simpler therapy choices, and a greater understanding of the mechanisms that trigger delirium.
“What’s happening within the mind?” Hui requested. “What predictive biomarkers will assist us to grasp which affected person would profit extra from one therapy greater than the opposite?”
For now, prescribing schedule lorazepam or haloperidol makes “a number of sense” to scale back persistent agitation on the finish of life, he added.
“Be extra proactive than reactive,” Hui stated.
For extra data:
David Hui, MD, MSc, FAAHPM, may be reached at dhui@mdanderson.org.