Extremely-processed meals related to colorectal most cancers precursor
December 26, 2025
5 min learn
Key takeaways:
- Extremely-processed meals consumption was related to growth of typical adenomas, a precursor to early-onset colorectal most cancers.
- Extremely-processed meals didn’t have an affiliation with serrated lesions.
People who devour greater quantities of ultra-processed meals might have a considerably greater probability of growing a precursor situation to early-onset colorectal most cancers.
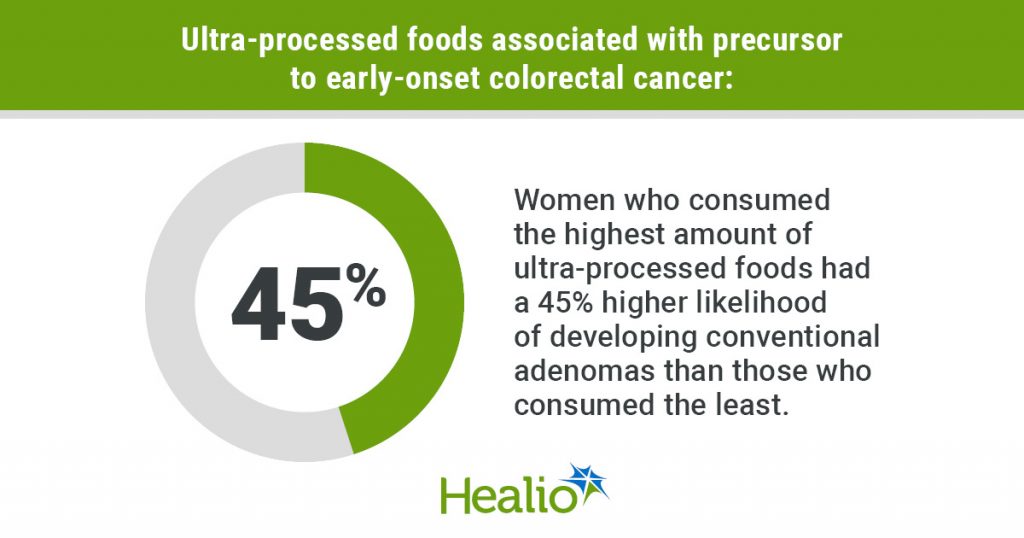
A research of almost 30,000 nurses confirmed those that ate probably the most ultra-processed meals had a forty five% larger probability of being identified with typical adenomas than those that ingested the least quantity.

Knowledge derived from Wang C, et al. JAMA Oncol. 2025;doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2025.4777.

Andrew T. Chan
“Our research presents one clue into one other potential threat issue for the rising incidence of early-onset colorectal most cancers,” Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, chief of the medical and translational epidemiology unit at Massachusetts Basic Hospital and Daniel Ok. Podolsky Professor of Medication at Harvard Medical Faculty, informed Healio.
“We urgently must attempt to discover causes for why this pattern is accelerating,” he continued. “Understanding extra about what’s modified in our eating regimen is one strategy, and our knowledge counsel that we’ve got to fastidiously think about our consumption of ultra-processed meals as a possible threat issue. That is laying the groundwork for extra research during which we are able to perceive whether or not these associations are trigger and impact, and the underlying mechanisms by which ultra-processed meals may result in colorectal most cancers extra broadly.”
‘Alarming improve’
Healio beforehand reported that 10% to 12% of colorectal most cancers circumstances happen amongst people aged youthful than 50 years.
Early-onset colorectal most cancers incidence has elevated 2.4% yearly between 2012 and 2021. Globally, charges rose 30% throughout the first 20 years of this century.
“It’s an alarming improve,” Chan mentioned.
The explanations for elevated incidence have been broadly investigated. Threat components can embrace weight problems, lack of bodily exercise, kind 2 diabetes and dietary patterns, in response to research background.
Within the U.S., energy from ultra-processed meals, outlined as “industrially produced ready-to-eat or ready-to-heat merchandise that comprise minimal complete meals,” account for roughly 60% of an grownup’s consumption, Chan and colleagues wrote.
“Provided that there have been many alternative detrimental well being results of ultra-processed meals which have been documented during the last a number of years, we puzzled whether or not there was a hyperlink,” Chan informed Healio. “May a few of the improve in early-onset colorectal most cancers be associated to this improve in publicity to ultra-processed meals?”
Researchers used the Nurses’ Well being Examine II, a potential cohort of feminine nurses within the U.S. born between 1947 and 1964, to research.
They included 29,105 individuals (imply age, 45.2 years; customary deviation, 4.5) who had documented dietary assessments and at the very least one decrease endoscopy after baseline however earlier than they reached age 50 years. Additionally they couldn’t have a historical past of non-melanoma most cancers.
Incidence of early-onset colorectal most cancers precursors — typical adenomas and serrated lesions —served as main endpoints.
‘We weren’t shocked’
Extremely-processed meals accounted for 34.8% of the cohort’s every day caloric consumption and 28.2% of its dietary servings, with a median of 5.7 servings per day (interquartile vary, 4.5-7.4).
The most typical ultra-processed meals consumed included breads and breakfast meals (22.6%); sauces, spreads and condiments (21.9%); and sugar-sweetened or artificially sweetened drinks (19.7%).
The cohort had a complete of 1,189 identified early-onset typical adenomas and 1,598 serrated lesions.
Ladies within the highest quintile of ultra-processed meals consumption had a considerably greater probability of growing typical adenomas (adjusted OR = 1.45; 95% CI, 1.19-1.77). Nonetheless, researchers didn’t observe a major distinction for serrated lesions.
“These two various kinds of polyps characterize distinct pathways by which colorectal cancers develop,” Chan mentioned. “There are some shared threat components however there’s additionally some distinction in threat components.”
“Early-onset colorectal most cancers most likely arises primarily by way of adenoma polyps. Based mostly on this, we weren’t shocked that the affiliation between ultra-processed meals and adenomas was extra pronounced than for serrated lesions, It suggests that there’s a molecularly particular impact of ultra-processed meals on cancers that develop by way of this adenoma precursor.”
The affiliation between ultra-processed meals and standard adenomas remained constant after adjusting for BMI, dietary components, kind 2 diabetes and different colorectal most cancers threat components.
“Amongst cancers, colorectal most cancers is the one which appears to be probably the most associated to eating regimen, and given what we all know in regards to the results of ultra-processed meals on different well being outcomes and on intestine well being, we weren’t shocked to see what we discovered,” Chan mentioned.
Ladies within the highest quintile of artificially sweetened beverage consumption had a considerably greater probability of being identified with typical adenomas (aOR = 1.21; 95% CI, 1.01-1.46).
Researchers acknowledged research limitations, together with the cohort being primarily “well-educated feminine nurses.”
“We have to attempt to confirm these findings in different populations that characterize a special slice of our inhabitants to know how generalizable the outcomes are,” Chan mentioned. “I believe, although, the associations between ultra-processed meals and most cancers are possible by way of mechanisms which can be vital no matter intercourse, occupational background, race and ethnicity. There’s an excellent foundation to consider that these associations are related to many people.”
‘Considered one of a number of threat components’
The magnitude of impression ultra-processed meals had on typical adenomas indicated it’s “certainly one of a number of threat components” possible resulting in the rise in early-onset colorectal most cancers incidence, Chan mentioned.
“It actually shouldn’t be the one reply,” he continued. “I believe that’s actually the subsequent step within the work, to attempt to perceive to what extent does this contribute to what we’re seeing when it comes to rising incidence. Additionally, are there particular methods we are able to higher characterize ultra-processed meals to know if there are particular meals gadgets which can be of explicit hurt?”
One other essential a part of future analysis is to judge trigger and impact.
“Our research was an affiliation research,” Chan mentioned. “We wish to have the ability to develop extra knowledge to be extra definitive about whether or not there’s a cause-and-effect relationship. A few of that shall be associated to making an attempt to know extra about what mechanisms could be underlying this affiliation, and why is it that these kinds of meals may contribute to colon most cancers threat.”
That might result in extra analysis into the intestine microbiome.
“I believe that’s a pure place to look,” Chan mentioned.
The analysis shouldn’t focus solely on colorectal most cancers although. The problems concerning ultra-processed meals elevate extra questions.
“How aggressive can we must be about decreasing our consumption of ultra-processed meals, provided that they’re so fashionable and are a supply of simple energy for our inhabitants?” Chan requested. “We might want to higher perceive the totality of dangers related to these kinds of meals, and what are practical methods we are able to attempt to cut back consumption within the normal inhabitants.
“We are able to actually encourage folks to make particular person selections, however there are limitations in that. In the end, there are questions round whether or not we have to do extra when it comes to meals labeling or different coverage efforts to attempt to cut back the ever-present nature of ultra-processed meals within the American eating regimen.”
For extra info:
Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, may be reached at achan@mgh.harvard.edu.








